Economic history of Peru
The has its traditional roots in natural sources such as for example mining, agriculture, fishing, and farming. In precolonial times, throughout the reign of Inca empire, the economic climate ended up being primarily agricultural, though it achieved some pet husbandry and mining development. The main aim of the Incan economic climate ended up being substinence, with a system predicated on reciprocity and change of services and products.
In recent years, there has been an apparent upsurge in slight sectors, solutions, and high technologies. In 2007, the Peruvian economy expanded 9per cent, the greatest development price worldwide.
Pre-colonial[edit]
The Tahuantinsuyo ended up being arranged in dominions with a stratified community, in which the ruler had been the Inca. It absolutely was also sustained by an economy on the basis of the collective home regarding the land. Indeed, the Inca Empire ended up being conceived like an ambitious and audacious civilizing task, considering a mythical thought, in which the balance of this interactions involving the individual, nature, and gods had been really essential. The economy ended up being mainly farming, though it reached some animal husbandry and mining development. The primary aim of the Incan economic climate was substinence, with a method considering reciprocity and trade of items
Colonial[edit]
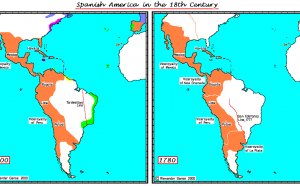
The colonial economy had been dominated by mineral wealth, and work was initially offered through enslavement of indigenous peoples. Peru’s valuable mineral sources and large indigenous population placed it within core regarding the South United states colonies; relating to Palmer, Peru could be ranked second on a scale of colonial penetration (Mahoney, 66). Textiles, minerals, and sugars through the colonies had been shipped returning to European countries.
Following the war of succession of 1700, Spain begun to lose its monopoly over colonial trade. Within the mid-18th century, liberal factions started initially to appear in the colonial elite; these asked the legitimacy of the crown’s rule inside Americas. These “Creole patriots”, which had originally already been marginalized to the periphery of kingdom (Venezuela, Argentina, etc.), offered the mandatory circumstances for effective financial development during the late colonial duration (Mahoney, 52, 80). The development of free-trade led to volatile growth through the entire empire, with Spain receiving ten times even more imports by the end for the 18th century. Not surprisingly overall growth of the colonies, the trend seen in Peru over the course of the century . 5 following the war of secession ended up being one of stagnation. The local socioeconomic hierarchy inverted itself, as core regions in which liberals were missing skilled far lower quantities of financial development. Their particular marginalization actually allowed them to benefit from expanded trade options. According to Mahoney, “regional experts have argued that underdevelopment throughout [areas like Peru] are tracked to colonial habits of economic reliance, Hispanic tradition, and inefficient markets and financial arrangements".
Wanting to protect its colonial belongings and reverse its faltering part in colonial trade, the top applied liberalizing reforms, hastening the removal of trade constraints and weakening colonial monopolies. This proceeded the decay associated with core regions, leaving all of them more subjected to the uncertainties associated with no-cost market. Because of the mid-19th century, the reversal of the socioeconomic hierarchy ended up being full; Peru would not recuperate its Viceroyalty-era supremacy (Mahoney, 86).
Post-colonial[edit]
Peru embarked in a railway building program. Henry Meiggs built a regular gauge line from Callao over the Andes towards Indoor, Huancayo; hitting for Cuzco he built the range but additionally bankrupted the nation.
In 1879, Peru joined the War associated with the Pacific which lasted until 1884. Bolivia invoked its alliance with Peru against Chile. The Peruvian Government attempted to mediate the dispute by sending a diplomatic staff to negotiate with the Chilean government, but the committee concluded that war was inescapable. Chile declared war on April 5, 1879. Nearly five years of war ended because of the loss in the division of Tarapacá and the provinces of Tacna and Arica, in Atacama area.
Initially Chile invested in a referendum for the towns of Arica and Tacna becoming held many years later on, so that you can self determine their particular nationwide affiliation. However, Chile refused to make use of the Treaty, and both nations could not determine the statutory framework. In an arbitrage that both nations admitted, the USA decided that plebiscite had been impractical to simply take, for that reason, direct negotiations between the functions led to a treaty (Treaty of Lima, 1929), in which Arica had been ceded to Chile and Tacna remained in Peru. Tacna gone back to Peru on August 29, 1929. The territorial reduction together with substantial looting of Peruvian locations by Chilean troops left scars regarding nation's relations with Chile that have not however totally healed.
After the War associated with the Pacific, a fantastic effort of rebuilding began. The federal government started initially to start numerous social and financial reforms being recover from the damage of this war. Political stability had been attained just in the early 20th century.
twentieth century[edit]
On October 29, 1948, General Manuel A. Odría led an effective military coup and became the newest President. Thanks to a thriving economy, Odría could apply high priced, populist social repair, including housing projects, hospitals, and schools. His government was dictatorial, but and civil-rights were seriously limited, and corruption ended up being rampant throughout his régime.
Armed forces juntas continued to majoritarily rule Peru across next three years. The economic guidelines associated with 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s particularly, had been in line with the substitution of imports, and had small impact on how big the economic climate. General Francisco Morales Bermúdez changed leftist General Juan Velasco Alvarado in 1975, mentioning Velasco's financial mismanagement, among various other elements. Morales Bermúdez brought about an even more conservative period, beginning the duty of rebuilding the united states's economy.
In 1980, after 12 many years of military rule, Fernando Belaúnde Terry was chosen President. After a promising start, their appeal eroded underneath the stress of inflation, economic hardship, and terrorism; their federal government's warm liberalization attempt failed into the framework for the Latin-American debt crisis, as per capita income declined, Peru's foreign financial obligation burgeoned, and violence by leftist insurgents (notably Shining Path) rose steadily during internal dispute in Peru, that was launched the day before Belaúnde's election. He proceeded most of the jobs that have been in the offing during his 1963-1968 term, including the conclusion associated with the Carretera Marginal de la Selva, a roadway connecting Chiclayo on the Pacific coast with then-isolated northern areas Amazonas and San Martín.
Through the after that years, the economic issues left out because of the junta government persisted, worsened by an event of climate trend in 1982–83, which caused widespread flooding in some areas, serious droughts in other individuals, and decimated the schools of sea seafood being one of several country's significant resources.
RELATED VIDEO



Share this Post
Related posts
Tours of Peru and Galapagos
Discover the organic marvels for the Galápagos in addition to magnificent social treasures of Peru. Explore the ancient Inca…
Read MoreViceroyalty of Peru
Viceroyalty of Peru Spanish Virreinato de Peru, the 2nd for the four viceroyalties that Spain designed to control its domain…
Read More